Today, the security of sensitive information and digital assets is a top priority for organizations globally.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework 2.0 stands as a potent and adaptable instrument, aimed at aiding organizations of varying sizes in navigating the intricate terrain of cybersecurity. Developed by NIST, a renowned authority in technology and standards, the framework has achieved broad recognition and adoption. This article delves into the NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0, offering an in-depth view of its purpose, core functions, and the extensive benefits it offers to organizations.
Join us as we lay the foundation for a month of in-depth exploration into this essential cybersecurity resource.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework’s primary role
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework’s primary role is to offer a structured methodology for organizations to effectively understand, assess, prioritize, and communicate cybersecurity risks. In today’s interconnected world, where data is vital to organizational operations, cybersecurity threats pose severe repercussions, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. A systematic approach is necessary for organizations to comprehend their current cybersecurity posture, identify and prioritize risks, implement protective measures, respond efficiently to incidents, and enhance communication regarding cybersecurity risks.
Continuous Improvement and Stakeholder Engagement
A key aspect of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0 is its emphasis on continuous improvement, encouraging organizations to consistently refine their cybersecurity strategies and practices . Additionally, the framework’s development involved substantial input from stakeholders, offering avenues such as workshops and public comment submissions, ensuring its relevance and adaptability in addressing evolving cybersecurity challenges .
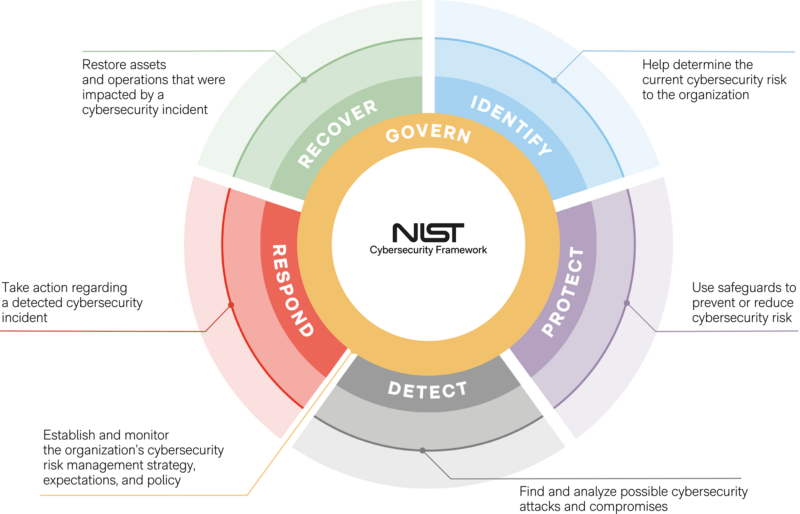
The heart of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0 is its Core, which now includes seven essential functions, with the recent addition of “Govern.” This new function underscores the need for oversight in the governance process, resonating with the ethos of ISO 27001, which requires regular internal audits and management reviews. The “Govern” function also aligns with the management of supply chain risks, advocating a strategic approach to handling risks related to vendors and third-party services, similar to ISO 27001’s Supplier Relationship clauses.
Introducing the CSF 2.0 Reference Tool
A notable development is the introduction of the Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0 Reference Tool by NIST. This tool allows users to explore the Draft CSF 2.0 Core, offering human and machine-readable versions, aiding in creating customized versions of the CSF 2.0 Core with selected informative references. This tool will be continuously enhanced with additional features, including Informative References, once CSF 2.0 is finalized in early 2024 .
NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0, redesigned by Ermes Cybersecurity
Understanding the Framework’s Purpose
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework, developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), serves as a critical guide for organizations seeking to enhance their cybersecurity posture. Its primary purpose is to provide a structured framework that empowers organizations to understand, assess, prioritize, and communicate about cybersecurity risks effectively.
Why is understanding and managing cybersecurity risks crucial?
In an increasingly interconnected world, where data is the lifeblood of organizations, cybersecurity risks can have severe consequences. These risks encompass a wide range of potential threats, from malicious hackers seeking unauthorized access to sensitive data to system failures that can disrupt operations. Moreover, the consequences of a cybersecurity breach extend beyond financial losses to reputational damage and legal liabilities.
To mitigate these risks effectively, organizations need a systematic approach that enables them to:
- Understand Their Current Cybersecurity Posture: Before addressing cybersecurity risks, organizations must gain a clear understanding of their existing security measures and potential vulnerabilities.
- Identify and Prioritize Risks: Not all risks are created equal. Some vulnerabilities pose a more significant threat than others. The framework helps organizations identify and prioritize risks based on their potential impact and likelihood.
- Implement Protective Measures: Armed with a thorough understanding of risks, organizations can implement protective measures to reduce their vulnerability to cyber threats.
- Respond Effectively to Incidents: In the unfortunate event of a cybersecurity incident, having a well-defined response plan in place is crucial to minimize damage and recover swiftly.
- Enhance Communication: Effective communication about cybersecurity risks is essential both within an organization and with external stakeholders. The framework promotes a common language for such communication.
Exploring the Framework Core Functions
The Framework Core is the heart of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0, consisting of seven essential functions, each meticulously organized to address key cybersecurity outcomes. These functions work in harmony to provide organizations with a comprehensive approach to managing and mitigating cybersecurity risks effectively.
GOVERN (GV):
This cross-cutting function serves as the foundation, involving the establishment and ongoing monitoring of an organization’s cybersecurity risk management strategy, policies, and expectations. It provides crucial guidance for achieving desired outcomes across all the other functions, taking into consideration the organization’s mission, objectives, and stakeholders.
IDENTIFY (ID):
At the core of the framework, this function focuses on identifying and understanding the current cybersecurity risks faced by the organization. It involves a meticulous examination of assets, including data, hardware, software, and facilities, as well as an in-depth analysis of related risks. This comprehensive understanding forms the basis for effective risk management.
PROTECT (PR):
The protect function is all about putting safeguards in place to prevent or reduce cybersecurity risks. It covers a wide array of critical aspects, including employee awareness and training, data security, identity management, authentication, access control, platform security, and the resilience of technology infrastructure. By implementing protective measures, organizations fortify their defenses against potential threats.
DETECT (DE):
In today’s fast-paced cybersecurity landscape, timely detection of potential threats is paramount. The detect function involves actively seeking and analyzing potential cybersecurity attacks and compromises. It enables organizations to swiftly discover and assess anomalies, indicators of compromise, and other warning signs that may indicate ongoing cybersecurity incidents or attacks.
RESPOND (RS):
When a cybersecurity incident is detected, a prompt and efficient response is imperative. The respond function comes into play at this critical juncture, guiding organizations in taking decisive actions. It supports the containment of incident impact and encompasses crucial aspects such as incident management, analysis, mitigation, reporting, and communication.
RECOVER (RC):
The recover function is a vital part of the framework, focused on the post-incident phase. It is about restoring assets and operations that have been impacted by a cybersecurity incident. The ultimate goal is to facilitate the timely recovery of normal operations, minimizing the impact of cybersecurity incidents and ensuring effective communication during the recovery efforts.
The Framework Tiers
In addition to the core functions, the NIST Framework introduces Tiers, which categorize an organization’s cybersecurity maturity. These Tiers range from Partial (Tier 1) to Adaptive (Tier 4). Organizations can assess their current Tier and aspire to advance to higher levels, signifying increased cybersecurity maturity.
What do the Tiers represent?
The Tiers represent different levels of cybersecurity maturity and resilience within an organization. They help organizations understand where they stand in terms of cybersecurity practices and provide a roadmap for improvement.
- Tier 1 – Partial: Organizations at this level have an ad-hoc approach to managing their organizational cybersecurity risk strategy. There is limited awareness of cybersecurity risks, and cybersecurity risk management is irregular. There are no established processes for sharing cybersecurity information.
- Tier 2 – Risk Informed: Organizations at Tier 2 have approved risk management practices in place. They prioritize actions based on risk objectives and the threat environment. There is increased awareness of cybersecurity risks, and some informal sharing of cybersecurity information occurs.
- Tier 3 – Repeatable: In Tier 3, organizations have formal risk management practices as policy. They take an organization-wide approach to managing cybersecurity risks, with consistent methods for responding to changes in risk. Regular monitoring and communication of cybersecurity risks are established, along with formal actions on cybersecurity risks in products, services, and supply chains.
- Tier 4 – Adaptive: The highest tier, Tier 4, involves an organization-wide approach using risk-informed policies. There is a clear understanding of cybersecurity risks in the context of objectives, and cybersecurity risks are integrated with other organizational risks. Adaptive cybersecurity practices based on lessons learned are in place, enabling real-time understanding and actions on cybersecurity risks. A governance structure is established for managing risks throughout the supply chain.
These Tiers provide organizations with a clear path to improving their cybersecurity resilience. By assessing their current Tier and aiming for advancement, organizations can continuously enhance their ability to protect against cyber threats.
Benefits of Implementing the NIST Framework
Implementing the NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0 offers numerous advantages for organizations of all sizes and across various sectors. Some of the key benefits include:
- Proactive Risk Management
The NIST Framework promotes a proactive approach to identifying and mitigating cybersecurity risks. By understanding their current cybersecurity posture, identifying vulnerabilities, and implementing protective measures, organizations can stay ahead of evolving threats. This proactive approach is essential in today’s rapidly changing threat landscape.
- Improved Communication
Effective communication is at the core of any successful cybersecurity strategy. The Framework’s emphasis on creating a common language for internal and external communication fosters collaboration among different stakeholders within the organization. It also improves information sharing, both within the organization and with external partners, facilitating a coordinated response to cyber threats.
- Potential Revenue Generation
Effective cybersecurity measures can build trust among customers and partners. When organizations demonstrate a commitment to cybersecurity and the protection of sensitive data, they can potentially open up new business opportunities and revenue streams. Customers are more likely to do business with organizations they trust to protect their data.
- Enhanced Resilience
Cybersecurity incidents can disrupt operations and damage an organization’s reputation. By implementing the NIST Framework, organizations can enhance their resilience to cyber threats. This includes measures to detect and respond to incidents swiftly, minimizing their impact and facilitating a quicker return to normal operations.
Conclusion
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0 stands as a valuable and adaptable tool for organizations seeking to navigate the complex landscape of cybersecurity. Its core functions, Framework Tiers, and proactive approach empower organizations to understand, assess, prioritize, and communicate about cybersecurity risks effectively. By implementing the Framework, organizations can take significant strides toward enhancing their cybersecurity posture and protecting their digital assets. In the weeks ahead, we will delve deeper into each core function, explore the concept of Framework Tiers, and discuss practical strategies for implementing the Framework effectively. Stay tuned as we uncover the secrets to bolstering your organization’s cybersecurity resilience with the NIST Framework.


Follow us on: